A new scientific partnership launched with TRICUSO
A new scientific partnership has been launched with TRICUSO (Three Research Infrastructures together: Carbon Uptake Southern Ocean). This four-year Horizon Europe funded project aims to improve the way carbon is observed and measured in the Southern Ocean — from data collection to data management.
THE SOUTHERN OCEAN - A KEY PLAYER IN THE CLIMATE SYSTEM
The Southern Ocean, which surrounds Antarctica, plays a major role in regulating the Earth’s climate. As a true carbon sink, it alone captures nearly a quarter of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities.
Yet its functioning remains poorly understood — its chemistry, biology, and flux exchanges are still subject to large uncertainties. Current models are not precise enough to accurately predict its influence on the climate. One of the main reasons is that this region of the planet is among the least observed, due to its extreme conditions and difficult accessibility.
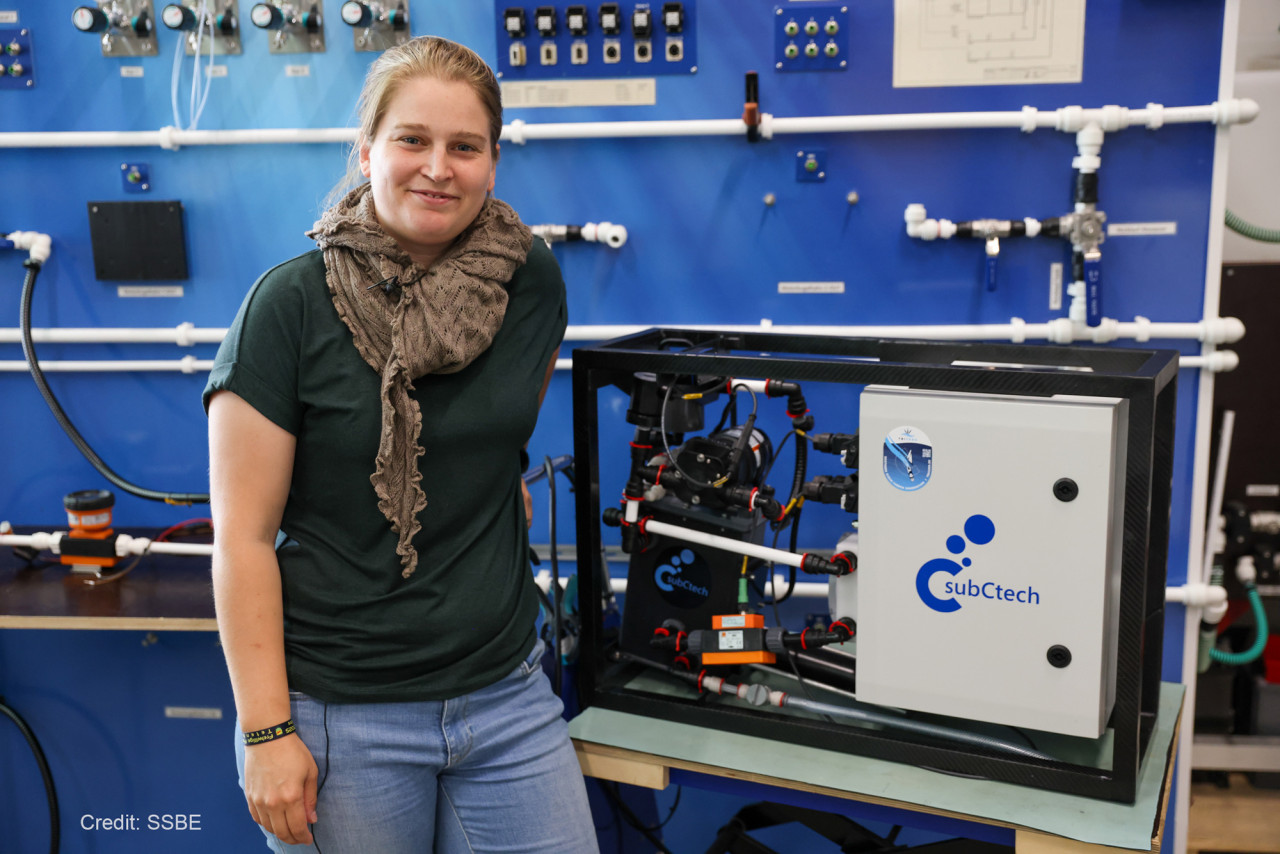
New sensors and sustainable solutions
The TRICUSO project aims to change that. It will develop new sensors and sustainable technologies to improve monitoring of this ocean. Researchers will rely on optimising ARGO floats — autonomous scientific platforms that dive deep into the ocean — as well as on citizen science, by installing high-tech sensors on ships of opportunity.
IMOCA, a partner for science
The IMOCA Class is joining this mission. During The Ocean Race in January 2027, one or more IMOCA boats will be equipped with the TRICUSO OceanPack sensor, a lightweight and innovative instrument designed to collect unprecedented data on carbon in the heart of the Southern Ocean.
Beyond scientific data collection, this partnership also aims to raise public awareness of the vital role the Southern Ocean plays in regulating the global climate. The next step will be to select the IMOCA teams that will carry the instrument on board for this scientific and oceanic adventure.
For more information, please visit the TRICUSO website.
Teams info
After a stunning 2025 season Sam Goodchild is the IMOCA Globe Series Champion for the second time
After a long season at the top of the IMOCA fleet that featured three race wins, Great Britain’s Sam Goodchild is for the second time in three years the IMOCA Globe Series Champion.
•••Quel rôle peut jouer la course au large dans la transformation du transport international ? Avec Pie…
Pour ce 10ᵉ épisode de Transitions, enregistré au Havre lors du départ de la Transat Café L'Or, nous recevons Jeremy Pochman, PDG de 11th Hour Racing, et Pierre-Antoine Morvan, responsable du pôle course au large et supe…
•••